|
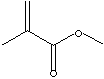
METHYL METHACRYLATE |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 80-62-6 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 201-297-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | H2C=C(CH3)COOCH3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 100.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
2916.14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 7872 mg/kg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | MMA; 2-Methyl 2-propenoic acid, methyl ester; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-(Methoxycarbonyl)-1-propene; 2-Methyl propenoic acid, methyl ester; Methacrylic acid, methyl ester; Methyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate 2-Methyl-2-propenoic acid methyl ester; 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, methyl ester; Acrylic acid, 2-methyl-, methyl ester; Metakrylan metylu (Polish); Methacrylate De Methyle (French); Methacrylsaeuremethyl Ester (German); Methyl 2-methyl Propenoate; Methyl 2-methyl-2-propenoate; Methyl apha-methyl Acrylate; Methyl-methacrylat (German); Methylester Kyseliny Methakrylove; Methylmethacrylaat (Dutch); Methylmethacrylate; Metil Metacrilato (Italian); MME; Methylpropylene-2-carboxylate; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DERIVATION |
esterification of methacrylamide sulfate with methanol |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
clear liquid |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT |
-48 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 101 C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.942 - 0.946 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 3.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
435 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 3; Reactivity: 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.4118
- 1.4125
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | 11 C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | The stability depends upon dissolved oxygen and MEHQ inhibitor. The presence of oxygen is necessary for inhibitor to prevent polymerization. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Acrylic acid is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid which has double bond
and carboxyl group in C3 one molecule with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. The vinyl
group is attached to the carbonyl carbon directly. The systemic name is
2-propenoic acid. Acrylic acid has two reaction points or functional groups
required for polymerization process. Purified (glacial) acrylic acid is a clear,
colorless liquid with a characteristic acrid odor. It is miscible with water,
alcohols and ethers. Acrylic acid is produced from C 3 refinery. Acrylic acid
undergoes the typical reactions of a carboxylic acid and forms acrylic esters -
basic alkyl esters are methyl, butyl, ethyl acrylate, and 2-ethylhexyl acrylate.
Acrylic acid and its esters undergo the reactions of the double bond which
readily combine with themselves or other monomers (e.g amides, methacrylates,
acrylonitrile, vinyl, styrene and butadiene) to form homopolymers or co-polymers
which are used in the production of coatings, adhesives, elastomers, super
absorbent polymers, flocculants, as well as fibres and plastics. Acrylate
polymers show a wide range of properties dependent on the type of the monomers
and reaction conditions.
Alkyl acrylates are clear, volatile liquid; slightly soluble in water and complete soluble in alcohols, ethers and almost organic solvents; Acrylate esters containing a double bond and functional carboxyl group are used chiefly as a monomer or co-monomer in making acrylic and modacrylic fibres. It is used in formulating paints and dispersions for paints, inks, and adhesives. It is used in making cleaning products, antioxidant agents, amphoteric surfactants. It is used in making aqueous resins and dispersions for textiles and papers. Methyl acrylate also used in making vitamin B1.
Methyl methacrylate (MMA) is ester of the unsaturated C4 carboxylic acid. The term of metha indicates an additional methyl group attached to the alpha carbon of acrylic acid. Methyl methacrylate is a flammable, colorless liquid; melting at -48 C, boiling at 101 C, soluble in the most organic solvents but insoluble in water. It is prepared by the esterification of methacrylamide sulfate with methanol. (The reaction of acetone and hydrogen cyanide forms acetone cyanohydrin, which is further treated with sulfuric acid to produce methacrylamide sulfate). Ammonium bisulfate is a byproduct. MMA is produced commercially also from C4 route ( isobutylene and tert-butyl alcohol) through two oxidation process. This process don't need sulphuric acid and no acidic by-products. MMA is the monomer to make polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) used as a shatterproof replacement for glass. It is a key ingredient in the production of cast and extruded acrylic sheet, acrylic emulsions, molding powders and extrusion resins. Polymers and copolymers of methyl methacrylate are also used in undissolved surface coatings, adhesives, sealants, impact modifiers, emulsion polymers, surgical bone cements, packaging applications, vinyl siding and other construction materials. Acrylics including (meth)acrylic acids, acrylic esters, and acrylic compounds containing reactive halogens, nitrile and amide groups are versatile monomers forming any class of hard, soft, resilient and transparent synthetic plastics or resins and viscous oils by varying the starting materials and the polymerization processes. The monomers can be either homopolymerized or be copolymerized with other type monomers capable of being polymerized. The resultant homopolymers can provide abundance hydrophilic property groups. Copolymers may be either hydrophilic or hydrophobic. Sodium acrylate is copolymerized with acrylamide to make an anionic copolymer used as a flocculant in water treatment. Acrylic esters copolymers with minor amounts of another functional monomer containing a reactive halogen or ethylenically unsaturated ester can form inter-linked polymer chains that display good heat and oil resistance. Homopolymers and copolymers have a variety of industrial applications including;
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear liquid |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PURITY |
99.8% min |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
COLOR, APHA |
10 max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FREE ACID |
0.005% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 0.942 - 0.946 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
WATER |
0.05% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
INHIBITOR |
5 ±1 ppm (Monomethyl Ether Hydroquinone) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TRANSPORTATION |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 180kgs in drum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | 3 (Packing Group: II) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. |
1247 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REMARKS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||